Nanoscale Biosensor Tracks Molecules in Real-Time
Scientists developed an ultra-sensitive nanoscale biosensor capable of tracking single molecules in living cells in real-time. This breakthrough technology allows unprecedented observation of cellular interactions and disease processes as they occur, dramatically enhancing biological research and drug testing.
Implications: Real-time monitoring at the molecular level could revolutionize drug discovery, disease diagnostics, and personalized medicine. However, practical implementation will require substantial technological integration and validation in clinical settings.
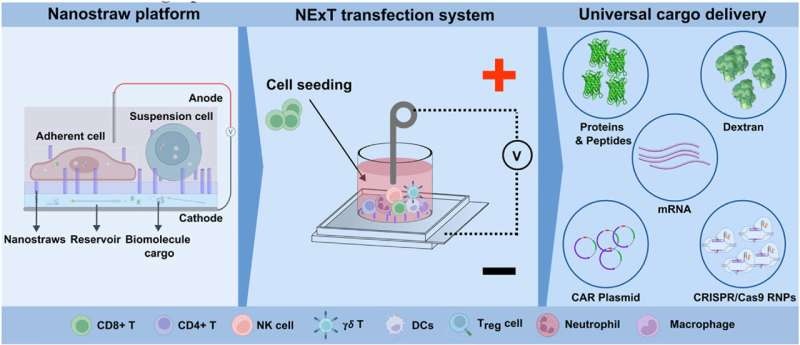
Nanostraws and Electrical Pulses Enhance Gene Delivery
A new approach using tiny "nanostraws" combined with brief electrical pulses significantly improves the delivery of genetic material directly into cells. This method boosts transfection efficiency while minimizing cellular damage, outperforming current viral and chemical-based gene transfer methods.
Implications: Enhanced gene delivery efficiency could accelerate gene therapies and cellular engineering, potentially making treatments safer and more affordable. However, safety profiles, scalability, and regulatory pathways remain critical considerations.
Newfound Mechanism for Drastic Weight Loss
Scientists have uncovered a novel biological mechanism that dramatically reprograms how cells process energy, leading to substantial weight loss in preclinical models. By targeting specific metabolic pathways, the researchers significantly increased calorie burn and improved metabolic health without altering diet or exercise routines. The discovery could pave the way for revolutionary obesity treatments.
Implications: If successfully translated to humans, this metabolic approach might provide a powerful new therapeutic option against obesity and metabolic syndrome. However, extensive clinical trials will be necessary to ensure long-term safety, effectiveness, and accessibility.
Dog Cancer Research Yields Insights for Childhood Osteosarcoma
A comparative oncology study has identified genetic and immunological similarities between canine and childhood osteosarcoma, leading to promising treatment insights applicable to both dogs and children. Early findings point toward new therapeutic targets that could benefit human pediatric patients.
Implications: Leveraging canine research may speed therapeutic development and improve outcomes for children. Yet, translating comparative findings into clinically effective therapies will require extensive validation and interdisciplinary collaboration.
High-Tech Contact Lenses Offer Superhuman Sight
Newly developed smart contact lenses offer enhanced vision capabilities, including zoom functions, night vision, and augmented-reality overlays, drastically extending natural human vision. Early trials indicate usability and safety, opening avenues for both medical and recreational applications.
Implications: Such advanced lenses could greatly assist visually impaired individuals and expand human sensory experiences, though broad adoption hinges on addressing privacy, ethical implications, and long-term eye health safety.
Vitamin D Supplements May Slow Biological Aging
A large-scale study found regular vitamin D supplementation significantly slowed markers of biological aging in adults. Participants showed improved cellular health and reduced inflammatory indicators associated with chronic aging diseases.
Implications: Vitamin D may represent a low-cost, accessible strategy to combat aging and chronic illness. However, individualized dosing, long-term effects, and interactions with other medications need further research before widespread recommendations are made.
Thank you for reading! Stay tuned for more discoveries pushing the boundaries of healthcare, biotechnology, and beyond.













Share this post