Brain Chip Restores Movement and Sensation
A groundbreaking brain-spine interface has enabled a patient with spinal cord injury to regain both movement and sensation. By decoding neural signals and transmitting them wirelessly to implanted electrodes, this chip successfully bypasses spinal damage, allowing voluntary limb control and sensory feedback for the first time.
Implications: This advancement could drastically improve quality of life for paralysis patients. However, significant challenges remain, including ensuring long-term stability, affordability, and patient-specific customization, which will determine widespread adoption.
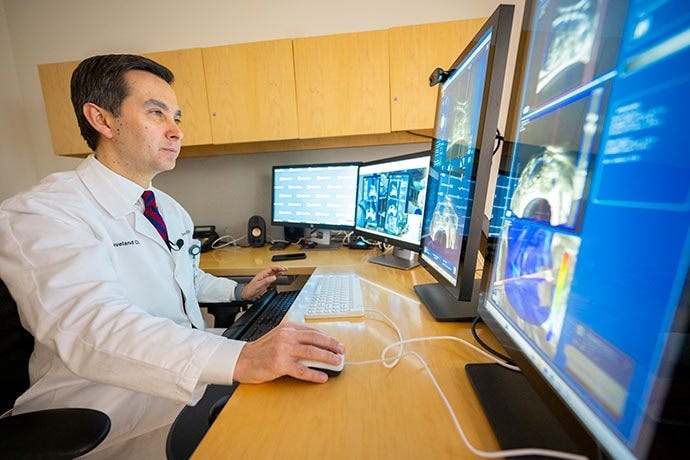
AI Monitors Blood Clots in Real-Time for Cardiac Patients
A new AI-powered system now provides cardiologists with real-time monitoring and predictive insights on blood clot formation. By accurately assessing clot dynamics during procedures, doctors can rapidly adjust treatments, reducing patient risks and improving outcomes.
Implications: Real-time AI diagnostics could significantly enhance procedural safety and precision in cardiology, though clinical adoption will rely on thorough validation, training protocols, and addressing data privacy concerns.
"Young Blood" Transfusions Enter Clinical Trials
Clinical trials investigating transfusions of young blood into older adults have begun, aiming to explore potential rejuvenating effects on aging-related biomarkers, cognitive function, and chronic disease risk. Early results indicate improvements in certain health indicators, sparking considerable scientific interest.
Implications: This controversial treatment could offer transformative benefits for aging populations if validated, yet significant ethical, regulatory, and safety concerns remain, necessitating rigorous oversight and public dialogue.
New Blood Test Predicts Disease Earlier
Scientists have developed a highly sensitive blood test capable of detecting disease biomarkers at earlier stages than current methods. Early validation trials showed impressive accuracy in identifying cancer and cardiovascular diseases well before symptoms emerged.
Implications: This non-invasive test could transform preventive medicine by enabling earlier, more effective interventions. Nevertheless, its effectiveness must be confirmed across diverse populations, and implications regarding healthcare accessibility and potential overdiagnosis must be addressed.
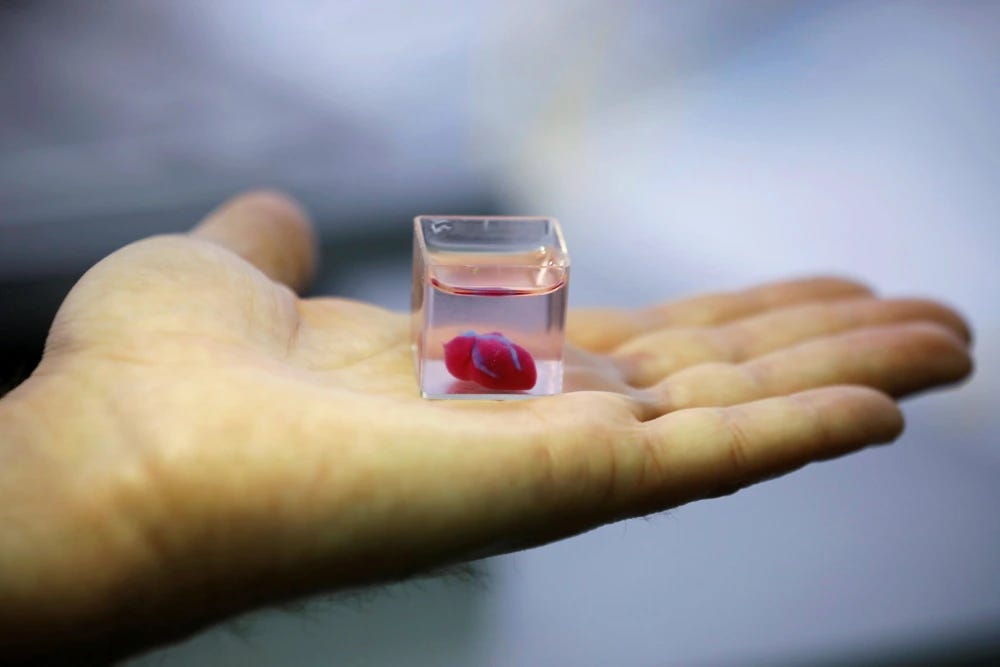
Custom CRISPR Therapy Saves Boy with Rare Genetic Disease
In an unprecedented case, doctors successfully used a personalized CRISPR-based therapy to correct a lethal genetic disorder in a young boy. The custom-designed gene-editing treatment reversed debilitating symptoms, significantly extending his life expectancy and quality of life.
Implications: Personalized gene-editing treatments could revolutionize rare disease care. Yet the high cost, lengthy regulatory processes, and ethical considerations of gene editing present substantial hurdles for broader application.
Mayo Clinic Discovery Improves Donor Heart Access
Researchers at Mayo Clinic have discovered a method to significantly extend the viability of donor hearts, potentially increasing the donor pool by preserving hearts longer and improving transplant outcomes. Early clinical applications demonstrated increased transplant success rates.
Implications: Expanding the pool of viable donor organs could save countless lives, yet implementation will require revising transplant protocols, managing resource allocation, and ensuring equitable access across patient demographics.
Surgeon Performs First-Ever Remote Surgery from 7,000 Miles Away
A surgeon successfully completed the world's first remote surgical operation from over 7,000 miles away using advanced robotic technology and real-time telecommunications. The procedure demonstrated comparable precision and outcomes to in-person surgery.
Implications: Remote surgery could dramatically expand specialized surgical access globally, especially in underserved regions. Still, broad adoption demands advanced infrastructure, robust fail-safes, and clear guidelines on legal liabilities and patient safety.
8-Hour Time-Restricted Eating Shows Long-Term Weight Loss Benefits
A recent long-term clinical trial found that participants who limited eating to an eight-hour window each day experienced significant and sustained weight loss, along with metabolic health improvements. The diet strategy proved effective without strict calorie counting or food-type restrictions.
Implications: This accessible dietary strategy could serve as a viable public health recommendation for weight management. However, further studies should address adherence rates, nutritional adequacy, and individual variability in response.
Thank you for reading! Stay tuned for more discoveries pushing the boundaries of healthcare, biotechnology, and beyond.















Share this post