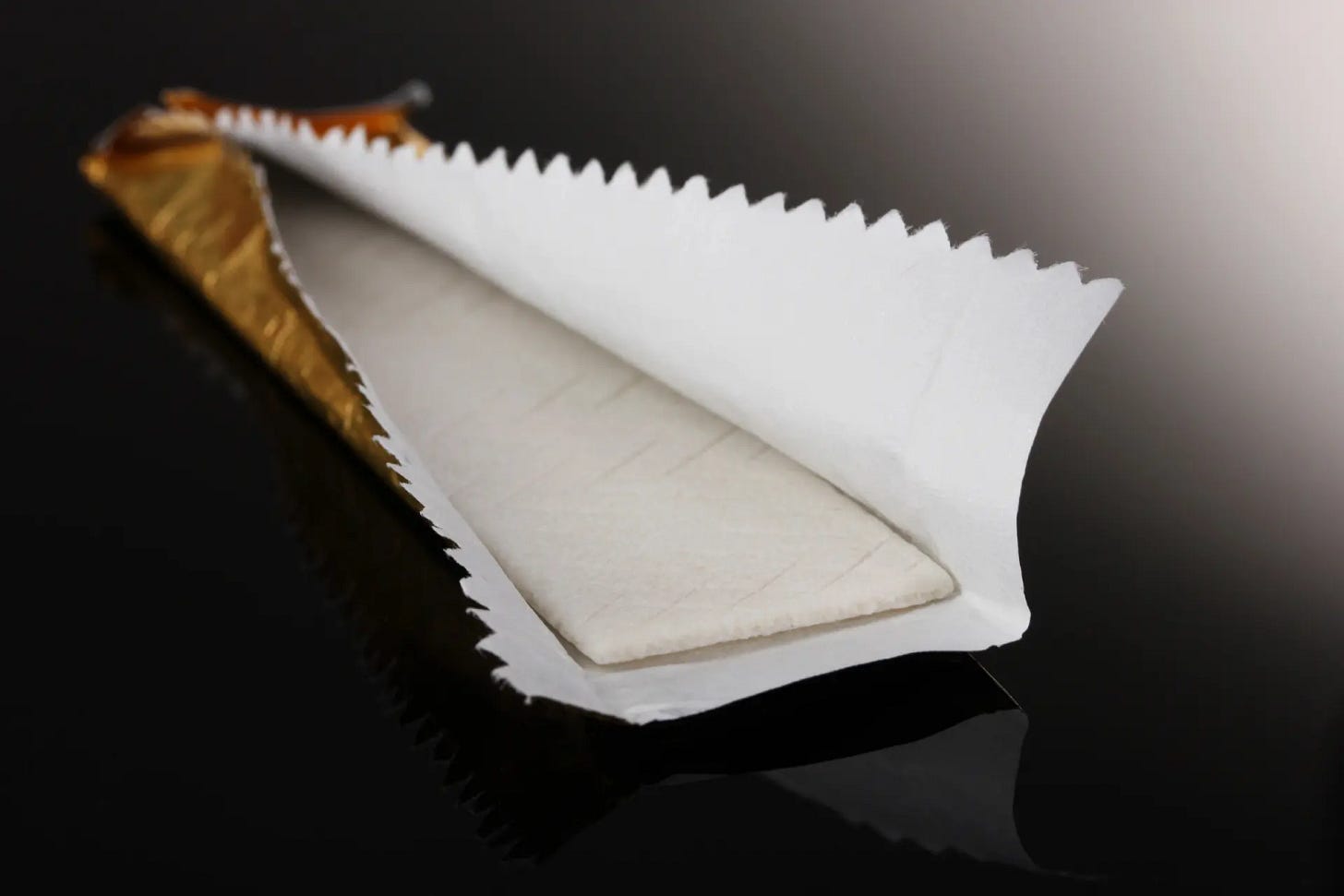
Antiviral Chewing Gum Blocks Flu & Herpes
Engineers embedded virus‑trapping plant proteins into chewing gum that captures influenza and herpes particles in saliva. Lab tests showed a 95 % drop in viral load after a few minutes of chewing, potentially reducing transmission. Human safety trials are now under way.
Implications: A simple, over‑the‑counter gum could add a low‑cost layer of protection during outbreaks, but real‑world efficacy and duration of action need validation.
Parkinson’s Cell Therapy Eases Symptoms
A small study implanted millions of lab‑grown dopamine‑producing neurons into patients’ brains. Most participants reported smoother movement and fewer tremors within months, with brain scans confirming graft survival and activity. Researchers will now track long‑term safety and refine dosing.
Implications: If larger trials replicate the gains, cell replacement could shift Parkinson’s care from symptom management to true functional restoration—though surgery costs and immune suppression remain hurdles.
Lab‑Grown Human Teeth Take Shape
Scientists coaxed human gum and stem cells to form tiny tooth buds that mineralized into early enamel and dentin layers in the lab. When transplanted into mice, the buds continued maturing, hinting at future fully formed bioteeth replacements.
Implications: Bio‑engineered teeth could one day replace implants and dentures, offering living, self‑renewing solutions—but scaling to adult‑sized, perfectly shaped teeth will demand significant bioengineering advances.
Japan’s Stem‑Cell Push Nears Clinical Payoff
A Nature report details how Japan’s investment in induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) is yielding early clinical successes—from retinal patches restoring vision to neuron grafts for spinal‑cord injuries. Regulators are streamlining approvals while demanding rigorous follow‑up.
Implications: If trials continue to show safety and benefit, iPSC‑based products could reach patients sooner in Japan than elsewhere, setting precedents for global regenerative‑medicine policy.
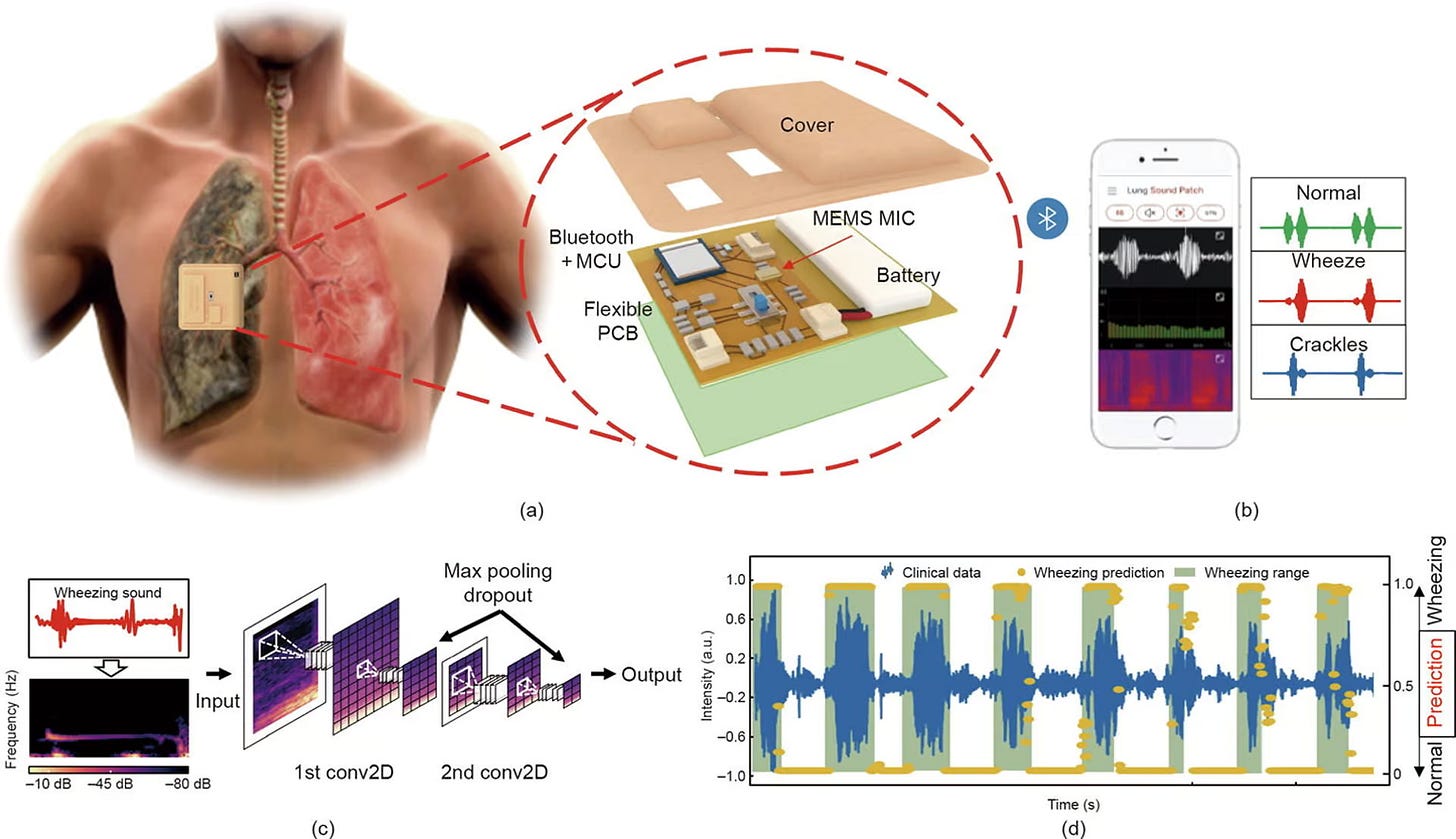
Wearable “Stethoscope Patch” Monitors Lungs
The LSMP patch sticks to the chest and records high‑fidelity lung sounds and breathing patterns, transmitting data to clinicians’ phones. In pilot tests, it detected wheezes and crackles linked to asthma and COPD exacerbations days before hospitalization.
Implications: Continuous, unobtrusive respiratory monitoring could enable early interventions, cut ER visits, and personalize treatment—provided data security and reimbursement paths are secured.
Fecal Transplants Show Promise for Autism
A randomized trial gave children with autism spectrum disorder microbiota transplants from screened donors. After eight weeks, recipients showed measurable improvements in social communication and reduced gastrointestinal distress versus controls. Benefits persisted at a six‑month follow‑up.
Implications: Modulating the gut–brain axis could become a therapeutic avenue for neurodevelopmental conditions, but larger, longer studies must confirm durability and rule out adverse effects.
Thank you for reading! Stay tuned for more discoveries pushing the boundaries of healthcare, biotechnology, and beyond.












Share this post