Google’s AMIE Gains Vision for AI Diagnostics
Google’s AMIE, an AI assistant for medical diagnosis, now incorporates multi-modal capabilities, combining visual data, dialogue, and textual medical records. Early trials demonstrate accurate preliminary diagnoses, helping clinicians prioritize complex cases.
Implications: Enhanced AI assistance could dramatically improve diagnostic speed and accuracy, though maintaining trust, transparency, and regulatory approval remains critical.
AI Agents Join Hospital Workforces
Hospitals are increasingly integrating AI agents as frontline support staff, managing tasks from patient triage and scheduling to routine documentation. Initial feedback from medical staff shows reduced burnout, improved efficiency, and higher patient satisfaction scores.
Implications: As AI takes over administrative and clinical support, healthcare staff may focus more on patient interactions, though privacy, reliability, and human oversight are paramount.
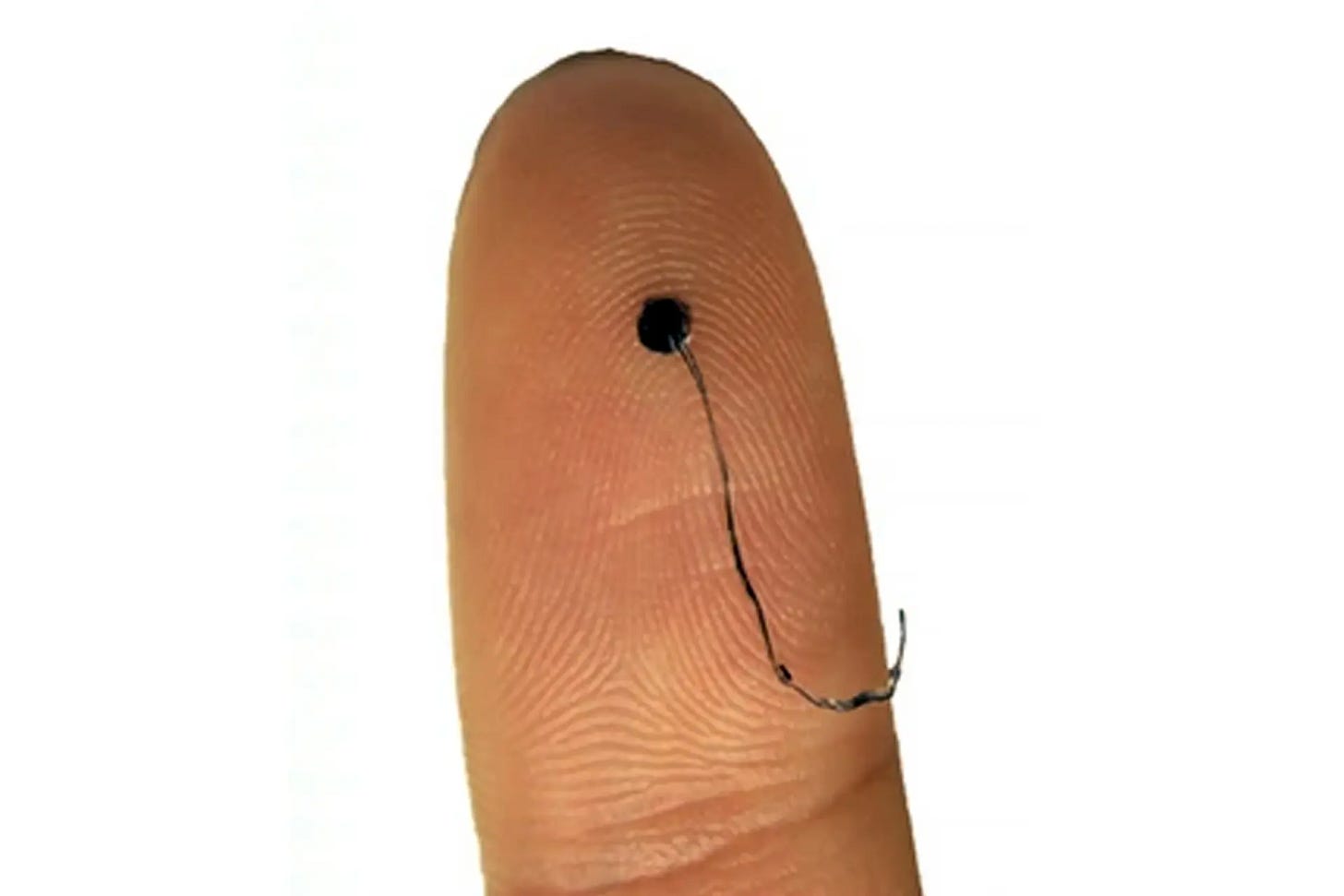
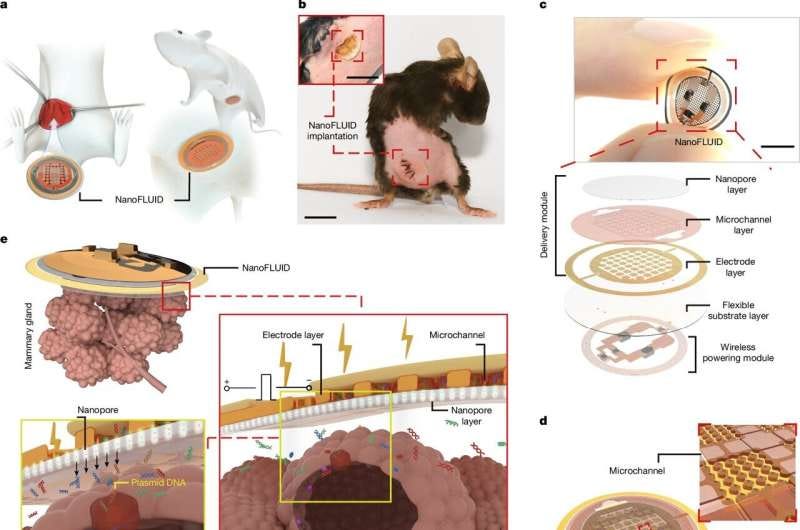
Electronic Band-Aid Accelerates Healing
Researchers unveiled a wearable "electronic band-aid" that uses electrical stimulation to boost healing of wounds and ulcers. Lab tests showed significantly faster tissue regeneration and reduced inflammation compared to standard dressings.
Implications: This tech could revolutionize wound care, particularly for chronic wounds, but further studies must ensure safety and efficacy in diverse clinical settings.
NIH Launches Universal Vaccine Platform
The NIH announced a major initiative for developing a universal vaccine platform targeting multiple pandemic-prone viruses simultaneously, leveraging advanced genetic and mRNA technology. Early research suggests high cross-protective immunity in animal models.
Implications: Success could transform global pandemic preparedness, but implementation requires extensive safety assessments, international collaboration, and broad public trust.
3D-Printed Hairlike EEG Electrodes for Better Brain Monitoring
A new EEG electrode, featuring ultra-thin, hairlike structures produced by 3D printing, captures brain signals more comfortably and clearly. Tests demonstrate higher accuracy in monitoring neural activity compared to traditional EEG devices.
Implications: Improved, minimally invasive brain monitoring could enhance diagnostics in epilepsy and sleep disorders, but translating to widespread clinical use requires rigorous validation.
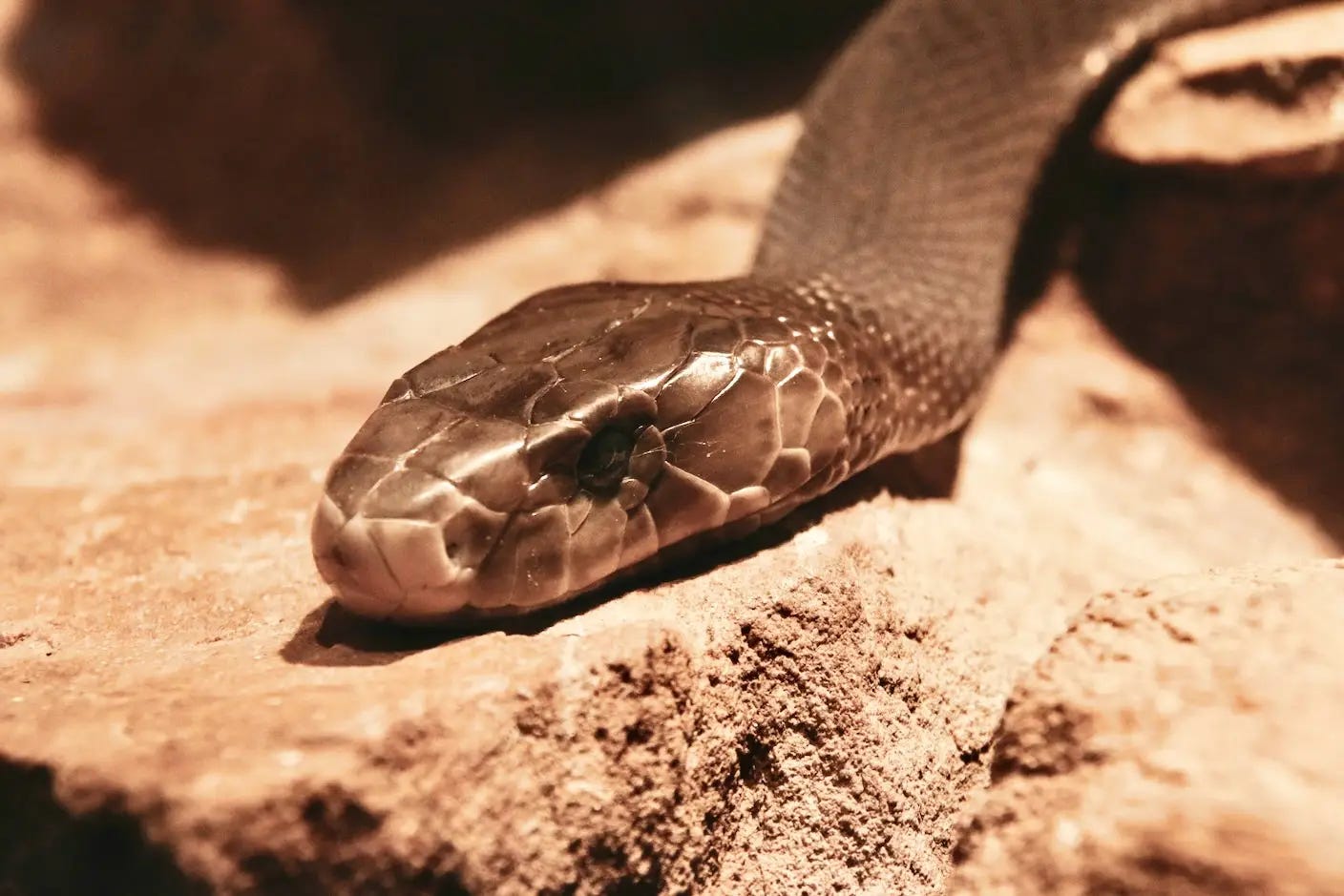
Blood of Man Who Survived Snakebites Holds Antivenom Clues
A man who survived hundreds of snakebites has blood uniquely rich in antibodies effective against multiple snake venoms. Researchers isolated these antibodies, potentially paving the way for universal, potent, and affordable antivenoms.
Implications: This discovery could save thousands globally, especially in remote regions—though production scale-up, testing, and affordability remain major challenges.
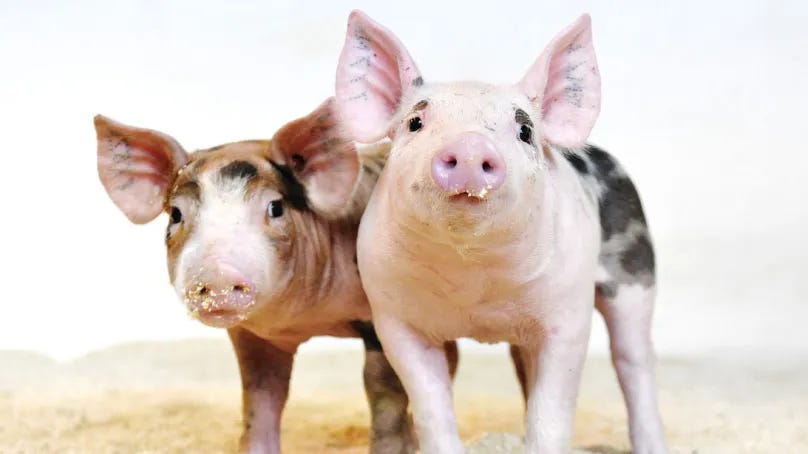
CRISPR-Edited Pigs Approved for Food in the U.S.
The U.S. government has granted approval for pigs genetically edited with CRISPR technology to enter the food supply. These pigs carry edits intended to improve animal health, growth efficiency, and disease resistance. The approval marks a milestone in agricultural biotechnology, paving the way for more genetically modified livestock entering markets.
Implications: CRISPR livestock could enhance food security and reduce antibiotic use, though consumer acceptance, ethical considerations, and regulatory oversight remain critical.
Thank you for reading! Stay tuned for more discoveries pushing the boundaries of healthcare, biotechnology, and beyond.















Share this post